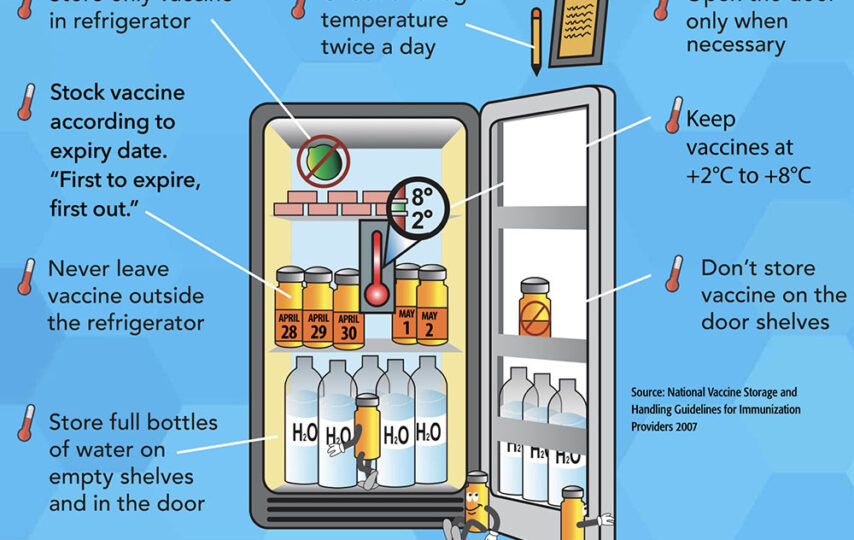
Vaccines are essential tools for preventing and controlling the spread of infectious diseases. However, to maintain their efficacy, vaccines must be stored under specific conditions, including temperature and humidity requirements. Proper storage is critical to ensure that vaccines remain effective and safe for use. Improper storage can lead to reduced vaccine potency, decreased efficacy, and even patient harm.
The impact of improper vaccine storage can be significant. Vaccines that are not stored within the recommended temperature range can lose their potency, meaning that they may not provide adequate protection against disease. Additionally, exposure to light, moisture, or temperature extremes can cause vaccines to break down or become contaminated, leading to potentially serious health risks for patients.
Therefore, healthcare providers must ensure that vaccines are stored properly to maintain their efficacy and safety. This requires strict adherence to recommended storage conditions, as well as proper handling, monitoring, and maintenance of vaccine storage equipment. In the following sections, we will discuss the proper storage requirements for vaccines, factors that can impact vaccine storage, and best practices for vaccine storage.
Proper Storage Requirements for Vaccines
The proper storage of vaccines requires strict adherence to specific temperature and humidity ranges. The recommended temperature range for vaccine storage typically falls between 2°C and 8°C (36°F to 46°F). The ideal humidity range is between 30% and 50%.
These requirements are necessary to ensure that vaccines remain stable and effective. Vaccines are biological products that contain live or inactivated organisms. They are sensitive to environmental factors such as temperature, light, and humidity. Exposure to temperatures outside the recommended range can cause vaccines to lose their potency, meaning that they may not provide adequate protection against disease.
Improper storage of vaccines can result in reduced vaccine efficacy, decreased patient immunity, and even patient harm. For example, a vaccine that has been exposed to temperatures outside of the recommended range may fail to provide adequate protection against the target disease. This could result in an outbreak of the disease, which could potentially harm patients, particularly those who are immunocompromised or otherwise vulnerable.
Proper storage of vaccines is essential to maintain their effectiveness and protect public health. Vaccines must be stored in a temperature-controlled environment, and the temperature must be monitored regularly to ensure that it remains within the recommended range. Healthcare providers must also take steps to prevent exposure to light, moisture, and other environmental factors that can impact vaccine stability.
Factors That Affect Vaccine Storage
Temperature fluctuations can occur due to several reasons, including equipment malfunctions, changes in ambient temperature, and improper handling of vaccines. Exposure to temperatures outside of the recommended range can lead to a loss of vaccine potency, rendering the vaccine ineffective.
The impact of temperature fluctuations on vaccine efficacy can vary depending on the severity and duration of the temperature excursion. If vaccines are exposed to temperatures outside of the recommended range for a short period, their efficacy may not be significantly impacted. However, if the temperature excursion is prolonged or severe, it can cause permanent damage to the vaccine and render it useless.
Power outages are also a significant risk to vaccine storage. Without power, refrigerators and freezers cannot maintain the appropriate temperature range, which can cause vaccines to become ineffective.
The consequences of power outages on vaccine efficacy can also vary depending on the duration of the outage and the temperature at which the vaccines are stored. If vaccines are stored in a freezer, they may remain effective for a longer period during a power outage than vaccines stored in a refrigerator. However, if the outage is prolonged, even vaccines stored in a freezer may become ineffective.
Best Practices for Vaccine Storage
Proper handling and storage of vaccines are essential to maintaining their efficacy. Healthcare providers must ensure that vaccines are stored at the correct temperature and humidity levels, as well as protected from light, moisture, and other environmental factors.
Strategies for monitoring and maintaining temperature control include using temperature monitoring devices, such as data loggers or digital thermometers, and performing regular temperature checks. Healthcare providers must also maintain backup power sources and develop protocols for responding to temperature excursions.
Protocols for responding to temperature excursions should include steps for identifying affected vaccines, isolating them from unaffected vaccines, and determining whether they can still be used. If vaccines have been exposed to temperatures outside of the recommended range, healthcare providers must contact their vaccine supplier or manufacturer for guidance on how to proceed.
By following best practices for vaccine storage, healthcare providers can ensure that vaccines remain effective and protect patients from preventable diseases.
Maintaining and Monitoring Vaccine Storage Equipment
Routine maintenance and calibration of vaccine storage equipment are crucial for ensuring that vaccines are stored at the correct temperature and humidity levels. Healthcare providers must follow the manufacturer’s guidelines for equipment maintenance and calibration, including regular cleaning and testing.
Strategies for monitoring and documenting temperature and humidity levels include using temperature monitoring devices, such as digital data loggers or thermometers, and documenting temperature and humidity levels regularly. These records should be kept for a minimum of three years and made available to regulatory agencies upon request.
There are several types of technology and equipment available for vaccine storage, including refrigerators, freezers, and ultra-low temperature freezers. It is essential to select equipment that meets the specific needs of the vaccines being stored, as different vaccines have different temperature requirements.
Compliance and Record Keeping
Regulatory requirements for vaccine storage vary by jurisdiction but often include guidelines for proper storage, handling, and transportation of vaccines. Healthcare providers must ensure that they comply with these regulations, as failure to do so can result in penalties, loss of licensing, and compromised patient safety.
Record keeping is an essential part of vaccine storage compliance. Healthcare providers must maintain accurate and complete records of vaccine inventory, storage temperature and humidity levels, equipment maintenance and calibration, and vaccine administration. These records should be kept for a minimum of three years and made available to regulatory agencies upon request.
Best practices for vaccine storage record keeping include using a vaccine inventory management system, documenting vaccine lot numbers, expiration dates, and storage temperatures, and regularly reviewing and updating records. Regularly reviewing and updating records can help identify potential compliance issues and prevent vaccine storage errors.
Conclusion
Proper vaccine storage is crucial for ensuring that vaccines remain effective and protect patients from preventable diseases. Healthcare providers must follow proper storage requirements and consider factors that can impact vaccine storage, such as temperature fluctuations and power outages. Best practices for vaccine storage include proper handling and storage of vaccines, monitoring and maintaining temperature control, and protocols for responding to temperature excursions. Routine maintenance and calibration of vaccine storage equipment, compliance with regulatory requirements, and proper record keeping are also essential for vaccine storage. By following best practices for vaccine storage, healthcare providers can help ensure patient safety and prevent vaccine storage errors.