Understanding the invisible forces between electric charges is key to grasping many important physics and engineering concepts. Yet calculating these forces precisely often requires wrestling with complex equations. Enter the world of convenience with a Coulomb’s Law calculator! This nifty online tool swiftly computes the electrostatic force’s magnitude between two point charges. No more grappling with formulas or juggling calculators; simply plug in the charge values and distance, and let the calculator handle the rest.
Now with a simple web-based Coulomb’s Law calculator, you can harness this key physics law. Forget struggling with equations – our calculator allows rapid calculation of electric force. Simply enter the charge quantities and distance, and it instantly computes the force using Coulomb’s formula. Understanding the theory is still important, but having an easy calculation tool is invaluable. Follow along as we explore the meaning of Coulomb’s Law, how to properly use the calculator, and the many applications across electrical engineering. Charge up your electrostatics knowledge with this guide to measuring electric force!
What is Coulomb’s Law?
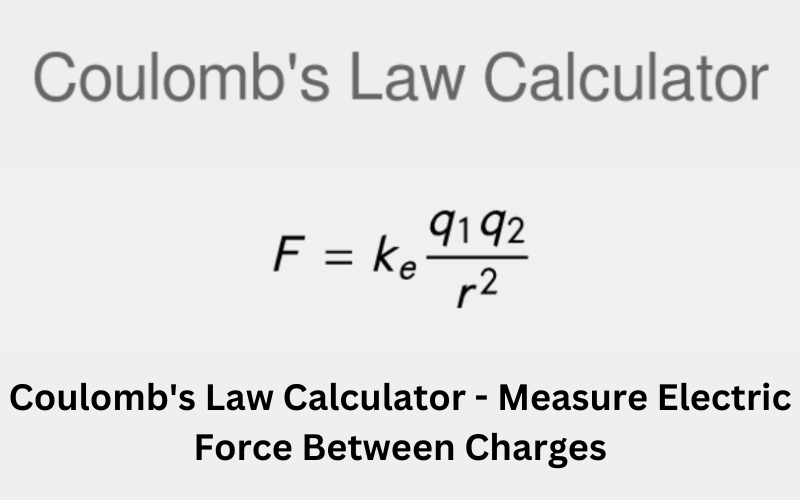
The law can be written mathematically as:
F = kq1q2/r^2
Where:
The magnitude of the force between charges is denoted by F, while q1 and q2 represent the magnitudes of the respective charges.
r is the distance between the charges
k is the Coulomb’s constant
So in plain English, as the distance increases, the force decreases rapidly as an inverse square relation. But if the charges increase, the force increases linearly.
Note that this fundamental law allows us to compute the forces between charges in any electrical engineering application imaginable. But the formula looks complicated, so how can we easily use it? Enter…the Coulomb’s calculator!
Coulomb’s Law Calculator Makes Life Easy
Forget wrestling with the formula; the Coulomb’s calculator simplifies the process. So, just input the necessary values, and let it crunch the numbers:
First up, enter the charge value (q1) of the initial particle in Coulombs (C).
Enter the charge value (q2) of the second particle in Coulombs
Enter the distance between the two charges in meters (r)
Note that the calculator automatically determines the electrostatic force using the Coulomb equation
It’s that simple! So, no more memorizing formulas or calculating by hand.
What are the Real-World Uses of Coulomb’s Law?
Electrostatic painting/printing – Charged particles are sprayed across a surface to deposit a patterned coating
Van de Graaff generators – Uses static electricity to demonstrate electrostatic effects and produce high voltages
Electrostatic precipitation – Charged plates attract and trap dust particles for air filtration
Parallel plate capacitors – Capacitance depends on the charges and distance between plates
Scanning electron microscopy – Uses electrostatic and electromagnetic lenses to focus a beam
Ion propulsion – Ions expelled to generate thrust for spacecraft navigation
Coulomb’s Law Calculator Usage Tips
To properly use Coulomb’s Calculator, keep these tips in mind:
Make sure all units are consistent. Use Coulombs (C) for charge and meters for distance.
Enter charge values as positive or negative to indicate repulsive or attractive force. Like charges are positive and negative.
The electrostatic force calculated is a vector quantity with direction. Imagine a straight line connecting the two charges.
For multiple charges, you can sum up the individual forces from each pair interaction.
For distributed charges over an area, integrate the charge to get the total q value.
For point charges (like electrons), make sure to enter very small distances like nano or micrometers.
With the ability to easily calculate electric force, you can gain deeper insights into electrical systems. The Coulomb’s calculator makes it a breeze!
What are Coulomb’s Law Fun Facts?
In delving into the intricacies of Coulomb’s Law, the enthralling historical narrative and captivating personalities contributing to this foundational physics concept often elude our grasp. The deployment of Coulomb torsion balances in the initial gauging of the electrostatic constant k serves as an evocative testament to the journey through the arcane corridors of early measurements. These novel instruments applied twisting forces to measure tiny electrical forces.
Coulomb originally wrote his law with forces in Newtons, but charge in ‘unites de charge’ rather than Coulombs. The Coulomb unit was named later in his honor.
The electrostatic constant k equals about 9 × 109 N·m2/C2. This constant reflects the property of space/vacuum to permit electric forces.
Coulomb studied friction and viscosity forces years before investigating electrostatics. He determined the mathematical laws governing both sliding and viscous friction.
As well as physics, Coulomb also contributed greatly to applied mechanics and civil engineering. He invented the Coulomb damper and studied stability and fractures.
The next time you use Coulomb’s calculator, remember the fascinating history behind it! Charles Coulomb’s pioneering work made modern electrical engineering possible.
So plug those charges in, calculate some forces, and appreciate the lasting legacy of a great 18th century physicist!
Conclusion
In our technologically advanced world, understanding electrical forces is more important than ever. From capacitive touch screens to wireless charging, electrostatics permeate our daily lives. Yet the fundamental laws governing these phenomena were established centuries ago. With his eponymous Coulomb’s Law, Charles Coulomb paved the way for our electrified society. By quantifying the intrinsic relationship between charge and force, he provided an essential mathematical foundation for electrical engineering.
So next time you pick up your smartphone or laptop, take a moment to appreciate the lasting legacy of Coulomb’s pioneering work. Our convenient online calculator makes Coulomb’s Law accessible and easy to apply. Simply enter a few parameters, and measure the invisible forces at play. Learning the theory is invaluable, but a handy calculation tool helps build true intuition. Charge up your knowledge of electrostatics, and power on your electrical insights. The world runs on the fundamental charge interactions Coulomb revealed so long ago. His inverse-square law of electric force is indeed a constant in our technological universe.
FAQs
Q1: What is the constant k in the Coulomb’s Law formula?
A: k is called Coulomb’s constant. It has a value of approximately 9 x 109 Nm2/C2. This constant reflects the intrinsic properties of the vacuum or space that permeate electric forces.
Q2: Can I calculate the net force between multiple charges?
A: Yes, you can sum up the individual forces calculated between pairs of charges using the principle of superposition.
Q3: Does Coulomb’s Law work for distributions of charge?
A: Yes, you can integrate a continuous charge distribution to find the total charge q and then use that value in the calculator.