Do you find yourself perplexed by the distinctions between flip-flops and latches? Are you unsure which one is better suited for your particular needs? If so, then you’ve come to the right place. This article provides an in-depth comparison of flip-flops and latches. Examining every aspect from their triggering mechanisms to their power consumption. By the time you finish reading, you’ll have a clear understanding of these two vital components in digital electronics. You’ll be able to determine which one is the most appropriate for your project. So, let’s delve into the realm of differences between flip flops and latches and explore the differences between them.
What is Flip Flop?
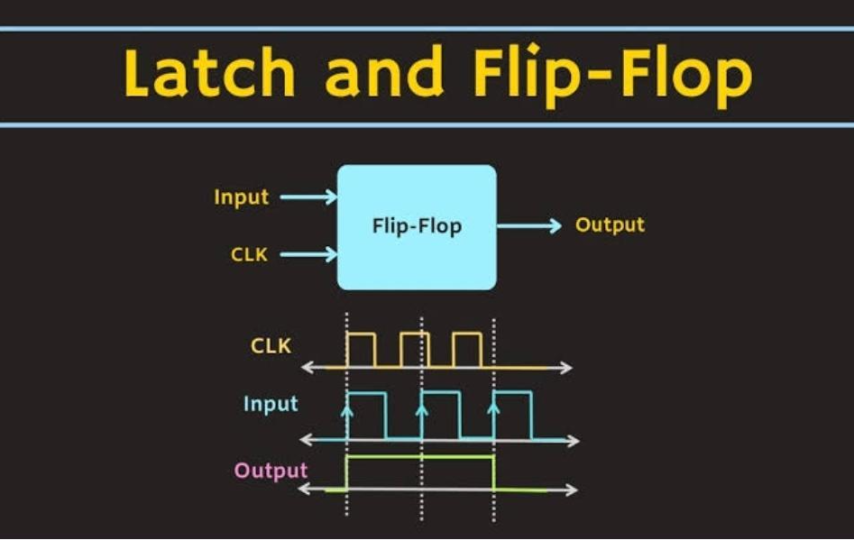
A flip-flop is an electronic component that can hold one bit of information in a stable state, with two possible states typically referred to as “0” and “1”. It is a fundamental building block for designing sequential circuits like registers, memory units, and counters. The SR flip-flop and D flip-flop are the most common types of flip-flops. The SR flip-flop is often used to implement logic gates, such as NAND and NOR. While the D flip-flop is commonly used in digital systems to store a single bit of data.
What is a Latch?
A latch is an electronic component that can hold one bit of information in a stable state. With two possible states typically referred to as “set” and “reset”. Unlike a flip-flop, a latch is level-sensitive. Meaning that its output is based on the input level at the time of a control signal transition. Latches can be used for transparent data storage, allowing data to pass through when the control signal is active. Holding the data when the control signal is inactive. Latches are widely used in digital systems to temporarily store data. Can be used as a building block to design more complex circuits, such as registers and memory units.
Flip-Flop vs Latch: Choosing the Right Circuit for Your Application
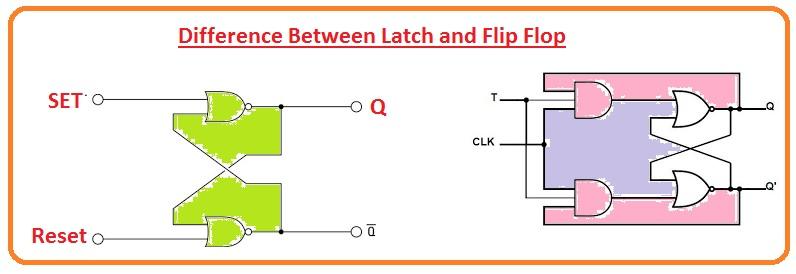
Image credit – The engineering knowledge
Flip-flops and latches are electronic components that are used in digital circuits to store data. Although they share some similarities, and also differences between flip flops and latches. A flip-flop is an electronic circuit that can hold one bit of information and has two stable states, usually identified as “0” and “1”. It is used as a building block for sequential circuits like registers, memory units, and counters. Flip-flops can be either edge-triggered or level-triggered. Meaning that they can be triggered by a signal edge or a signal level. The D, T, JK, and SR flip-flops are the most commonly used types.
In contrast, a latch is another type of electronic circuit. That can hold one bit of data and has two stable states, usually identified as “set” and “reset”. Unlike flip-flops, latches are level-sensitive. Meaning that their output depends on the input level at the time of a control signal transition. Latches are frequently used for transparent data storage. Which permits data to pass through the circuit while the control signal is active. Then holds the data when the control signal goes inactive.
To compare flip-flops and latches, the following table lists various aspects of these two circuits:
| Criteria | Flip-Flop | Latch |
| Storage | Can hold one bit of information | Can hold one bit of information |
| Stable States | Usually labeled as “0” and “1” | Usually labeled as “set” and “reset” |
| Triggering | Can be edge-triggered or level-triggered | Is level-sensitive |
| Outputs | Output a stable state | Outputs a signal level |
| Timing | Takes a finite amount of time to change state | Can change state immediately |
| Feedback | Can be used in feedback loops | Cannot be used in feedback loops |
| Applications | Used for building sequential circuits like registers, counters, and memory units | Used for transparent data storage and synchronization |
| Power Consumption | Consumes less power | Consumes more power |
| Complexity | More complex than latches | Less complex than flip-flops |
As the above table indicates, flip-flops and latches differ in their characteristics and are utilized in different applications. Flip-flops are commonly employed in sequential circuits. That needs to store and process data in a specific order, while latches are used for transparent data storage and synchronization.
Applications of Flip Flops & Latches
Here few applications of Flip Flops & Latches :
Flip-flops
- Flip-flops and latches have a wide range of applications in digital circuits and systems. Let’s explore some common uses of these two types of circuits.
- Flip-flops are commonly used in registers, which temporarily store data for processing.
- They are also used in counters, which count the number of pulses or events that occur.
- As well as in memory units like RAM and ROM. Additionally, flip-flops are used in timing circuits, such as clock dividers and pulse generators.
- They are also used to synchronize data between different clock domains.
Latches
- Latches are often used to hold data for a short period of time, allowing it to be processed further.
- They are used to store data temporarily until it is needed for processing.
- Latches are also used in bus interfaces, which connect digital circuits with buses.
- Furthermore, latches are used to condition digital signals, such as level shifting and signal isolation. Lastly, latches are used to implement state machines, which are critical components of digital control systems.
Frequently asked questions
Q: What is the main difference between flip-flops and latches?
A: The primary difference between flip flops and latch is their triggering mechanism. While flip-flops may be edge-triggered or level-triggered, latches are level-sensitive.
Q: In terms of speed, which is faster: a flip-flop or a latch?
A: Generally, latches are faster than flip-flops because they do not experience any delay during the clock cycle. Latches can change state immediately, while flip-flops require a finite amount of time to change state.
Q: What are some common uses of flip-flops?
A: Flip-flops are commonly used in registers, counters, memory units, timing circuits, and data synchronization.
Q: What are some common uses of latches?
A: Latches are used for data latching, data storage, bus interfaces, signal conditioning, and state machines.
Q: Which of the two is more intricate: a flip-flop or a latch?
A: Flip-flops are typically more complicated than latches because they require more components and a clock input.
Q: In terms of power efficiency, which is better: a flip-flop or a latch?
A: Latches are typically less power-efficient than flip-flops since they continuously consume power to maintain their output state. Flip-flops, in contrast, only consume power when their output state changes.
Conclusion
To sum up, flip-flops and latches have unique characteristics that make them suitable for different digital electronic applications. While flip-flops are well-suited for synchronous circuits, latches excel in asynchronous applications. Ultimately, the choice between the two depends on the specific needs of your project and the compromises you’re willing to make. By comprehending the differences between flip-flops and latches. You’ll be better prepared to decide which one is the most appropriate for your particular use case.
Also Visit: Quizizz: An Interactive and Fun filled Quiz-Making Platform