The Free Application for Federal Student Aid (FAFSA) is an essential process for students planning to attend college. Understanding how does FAFSA work is the first step. FAFSA is a form that collects financial details to determine your eligibility for various types of financial aid, including grants, loans, and work-study programs. This aid can come from the federal government, state government, or the college you plan to attend. The FAFSA application can be daunting, but breaking it down into manageable steps can help simplify the process.
Step 1: Gather Necessary Documents
To ensure a smooth application process, begin by gathering all necessary documentation. This includes your Social Security Number, which is critical for identification purposes. As a dependent student, you will need your parents’ financial information, including their tax returns, W-2 forms, and other money-earned records. Bank statements and records of investments may also be required if applicable.
Step 2: Create an FSA ID
Creating an FSA ID is a vital step in the FAFSA process. This unique username and password combination allows you to submit your FAFSA form electronically and access personal information on various U.S. Department of Education websites. The student and one parent need their own FSA IDs for dependent students.
Step 3: Start the FAFSA Form
The FAFSA form becomes available on October 1st each year and should be completed as early as possible. Early submission is key because some financial aid is awarded on a first-come, first-served basis. The easiest way to fill out the FAFSA form is online at the official website, but paper versions are available for those who prefer them.
Step 4: Fill Out Student Demographics
This section of the form is about your personal information. It includes questions about your name, date of birth, address, and other demographic information. This information helps the Department of Education identify you and determine your basic eligibility for financial aid.
Step 5: Provide Financial Information
In this crucial step, you’ll provide detailed information about your financial situation. This includes information from your tax returns, information about untaxed income, and details about assets such as savings and checking account balances. For dependent students, this section will also require similar information from their parents. Accurate financial information is vital for correctly determining your Expected Family Contribution (EFC), which is used to calculate the amount of aid you’re eligible to receive.
Step 6: Choose Colleges to Receive Information
You can list up to ten colleges to receive your FAFSA information. These colleges will use this information to determine the types and amounts of financial aid they will offer you. It’s important to include any college you’re interested in, as you don’t need to have made a final decision yet. Including a range of colleges ensures you’ll receive financial aid information for all your options.
Step 7: Review and Submit Your Application
After completing all sections, review your application thoroughly. Make sure all the information provided is accurate and complete. Any errors or omissions can delay the processing of your application and affect the amount of aid you receive. Once you’re confident that everything is correct, submit your application. You’ll receive a confirmation page and an email confirming your application has been submitted.
Step 8: Follow Up and Next Steps
After submitting your FAFSA, keeping track of its status is important. You can check this online using your FSA ID. Additionally, monitor any emails or correspondence from the colleges you listed, as they might request additional information or documentation.
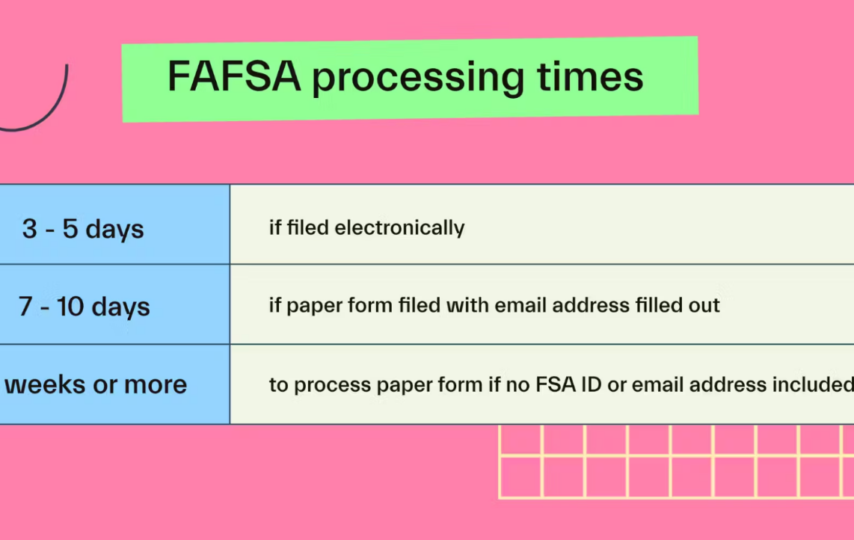
Ascent states, “It should take three to five days from the moment you submit your online FAFSA form for it to be processed.”
Navigating the FAFSA application process is critical in securing financial support for your college education. By understanding each step and preparing accordingly, you can ensure a smooth and successful application process.