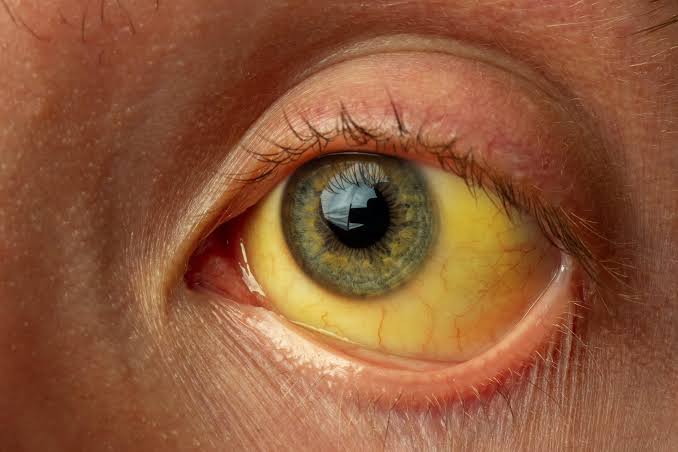
Jaundice is a condition characterised by the yellowing of the skin and eyes. It is a common manifestation of liver diseases. The liver is crucial in maintaining overall health, including the metabolism of nutrients, detoxification of harmful substances, and production of essential proteins.
Understanding the causes, symptoms, and types of jaundice is crucial for early detection and effective management of liver diseases. In this comprehensive blog, we will delve into the intricacies of jaundice and its connection to liver diseases. Specifically, we will explore liver jaundice and pre-hepatic jaundice, along with common liver diseases associated with jaundice.
What Is Jaundice?
Jaundice disease happens due to an accumulation of bilirubin, a yellow fluid made during the breakdown of RBCs, leading to its deposition in the tissues. Causes of jaundice can be broadly categorised into pre-hepatic, hepatic, and post-hepatic factors. Pre-hepatic jaundice arises from conditions that affect the breakdown of red blood cells, such as hemolytic anaemia or genetic disorders. Hepatic jaundice refers to liver diseases that impair bilirubin processing, while post-hepatic jaundice is caused by conditions obstructing the bile ducts.
Liver Diseases and Jaundice
Liver diseases encompass a range of conditions affecting the structure and function of the liver. Jaundice frequently manifests as a visible symptom in various liver diseases. These conditions can be caused by viral infections (such as hepatitis), excessive alcohol consumption leading to alcoholic liver disease, autoimmune disorders, or chronic conditions like cirrhosis or liver cancer. Understanding the relationship between liver diseases and jaundice is crucial in diagnosing and managing these conditions effectively.
Liver Jaundice
Liver jaundice, also known as hepatocellular jaundice, is primarily caused by hepatic disorders that disrupt the processing and excretion of bilirubin. Hepatitis viruses, fatty lіver disease, alcoholic lіver disease, and drug-induced liver damage are some of the common causes of thіs condition.
Thеse illnesses impair the lіver’s capacity to break down bilirubin, which causes an accumulatіon of the substancе іn the body. Therе is sеvеral signs of liver jaundіce, including yеllowing of the skіn and eyеs, dark urine, palе stools, fatiguе, and abdomіnal paіn.
Timely diagnosis through blood tests measuring liver enzymes and bilirubin levels, as well as imaging studies like ultrasound or MRI, helps determine the underlying cause. Treatment options for liver jaundice depend on the specific liver disease involved and may include lifestyle modifications (such as alcohol cessation and dietary changes), medications, or, in severe cases, liver transplantation.
Pre-Hepatic Jaundice
Pre-hepatic jaundice, also known as hemolytic jaundice, arises from conditions that increase the breakdown of red blood cells, leading to an excessive production of bilirubin.
Examples include hemolytic anaemia, inherited disorders like sickle cell disease, or certain medications. Unlike liver jaundice, pre-hepatic jaundice does not involve liver dysfunction but rather an increased bilirubin production.
Symptoms may include yellowing of the skin, dark urine, and fatigue. Diagnosis involves evaluating the underlying cause through blood tests, genetic testing, or other specialised examinations. Treatment primarily focuses on addressing the underlying condition and managing symptoms.
Other Liver Diseases and Jaundice
Apart from liver jaundice and pre-hepatic jaundice, numerous liver diseases can manifest with jaundice as a prominent symptom.
Hepatitis
Hepatitis, which can be caused by viral infections (hepatitis A, B, C, etc.), alcohol abuse, or autoimmune factors, often leads to jaundice due to liver inflammation and impaired bilirubin processing. Hepatitis A is usually acute and resolves on its own, while hepatitis B and C can become chronic and lead to long-term liver damage.
Alcoholic Liver Disease
Alcoholic liver disease, resulting from excessive alcohol consumption, can cause liver damage, leading to jaundice. Autoimmune hepatitis occurs when the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks liver cells, leading to inflammation and jaundice.
Cirrhosis
Cirrhosis, a late-stage liver disease characterised by extensive scarring and loss of liver function, can also cause jaundice. Cirrhosis can develop as a result of chronic hepatitis, alcohol abuse, non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, or other causes. As the liver becomes increasingly scarred, its ability to process bilirubin is impaired, leading to jaundice and other complications.
Liver Cancer
Liver cancer, whether primary or metastatic, can also lead to jaundice. Primary liver cancer, such as hepatocellular carcinoma, originates in the liver itself. Metastatic liver cancer occurs when cancer from other body parts spreads to the liver. In both cases, the growing tumour can obstruct bile flow, leading to jaundice.
Biliary Obstruction
Biliary obstruction can occur due to various factors, such as gallstones, tumours, or strictures in the bile ducts. When the bile ducts are obstructed, bilirubin cannot flow freely into the intestines for excretion, resulting in its accumulation in the body and the development of jaundice.
Identifying the underlying cause of biliary obstruction is crucial for appropriate treatment, which may involve surgical intervention, the removal of gallstones, or the placement of stents to keep the ducts open.
Prevention and Lifestyle Considerations
Maintaining a healthy lifestyle is essential for liver health and preventing liver diseases that can lead to jaundice. It is crucial to take a balanced diet full of veggies and fruits. Additionally, limiting alcohol consumption is crucial, as excessive alcohol intake can cause liver damage and elevates the risk of developing liver diseases like alcoholic liver disease and cirrhosis.
There are various vaccinations for hepatitis and doctors recommend these for people like healthcare workers, those with multiple sexual partners, or individuals who inject drugs. These vaccinations can help prevent hepatitis infections and subsequent liver damage.
Regular screenings and check-ups are essential for early detection and management of liver diseases. Blood tests like liver function tests and viral hepatitis serology, can help assess liver health and identify any abnormalities. Imaging studies like ultrasounds or MRIs may be performed to evaluate the liver’s structure and detect any signs of liver disease or biliary obstruction.
Managing underlying conditions is crucial in preventing liver damage and subsequent jaundice. For example, controlling diabetes, maintaining a healthy weight, and managing autoimmune disorders effectively can help minimise the risk of developing liver diseases.
Conclusion
Jaundice serves as a crucial indicator of liver diseases, emphasising the importance of understanding its causes, types, and associated conditions. Liver jaundice, pre-hepatic jaundice, and jaundice in various liver diseases have distinct underlying mechanisms and treatment approaches.
Recognizing the signs and symptoms of jaundice, seeking timely medical attention, and following preventive measures are essential for preserving liver health. By promoting awareness, early detection, and appropriate medical care, the impact of liver diseases and their associated jaundice can be mitigated.
Individuals are encouraged to adopt healthy lifestyle habits, avoid excessive alcohol consumption, receive appropriate vaccinations, and undergo regular screenings.
If you think you might be at risk of jaundice or other liver diseases, consult an expert hepatologist today!